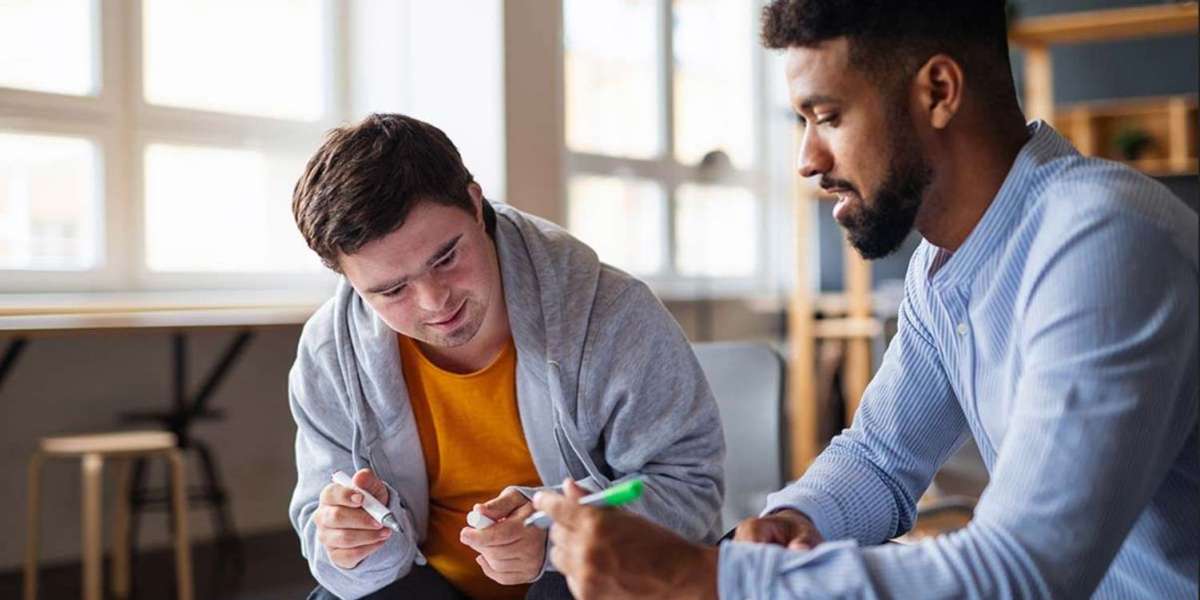
In today’s world, one of the most important goals is to ensure inclusion and a high quality of life for all members of society — including individuals with intellectual disabilities. To support this, a wide range of services for intellectual disabilities is available, covering everything from education and employment to medical and behavioral support.
What Are Intellectual Disabilities?
Intellectual disabilities are characterized by significant limitations in intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior, which covers social, communication, and daily living skills. These limitations may be present from birth or develop during early childhood.
What services for individuals with intellectual disabilities are available?
The range of services for intellectual disabilities is extensive and tailored to meet the diverse needs of individuals across all ages. These services are often designed to promote independence, support families, and facilitate full community inclusion.
1. Educational Programs
Education is the foundation for lifelong learning and development. For children and adolescents with intellectual disabilities, educational services may include:
- Special education schools, where students receive instruction in smaller classes with specialized teaching methods.
- Inclusive classrooms, which integrate students with disabilities into general education settings while providing individualized support.
- Early intervention programs for children under age three, focused on addressing developmental delays as early as possible through therapies and play-based learning.
- Individualized Education Plans (IEPs), developed through a team approach, set specific academic and functional goals and determine what services the student will receive.
These programs emphasize not only academics but also social, emotional, and life skills development.
2. Medical and Behavioral Support
People with intellectual disabilities often need specialized healthcare and behavioral interventions, including:
- Physicians familiar with developmental conditions, who can monitor overall health and manage co-occurring medical issues.
- Speech and language therapy, which helps with communication challenges — both verbal and non-verbal.
- Occupational therapy, to develop fine motor skills and improve performance in daily tasks like eating, dressing, and hygiene.
- Behavioral therapy, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), which is especially effective for individuals with autism or challenging behaviors.
- Psychiatric support, when mental health conditions like anxiety or depression are present.
These services aim to improve quality of life, foster independence, and promote emotional regulation and positive behavior.
3. Social and Day Programs
Day programs offer structured, supervised settings that help participants build practical and interpersonal skills. These may include:
- Day habilitation centers, where individuals engage in community activities, personal care training, and recreational events.
- Community-based programs, such as volunteer opportunities or local classes, that encourage social interaction and community inclusion.
- Life skills workshops, teaching cooking, budgeting, travel training, and other competencies for independent living.
These programs also provide important routines and a sense of purpose.
4. Supported Employment
Employment services help adults with intellectual disabilities find, secure, and thrive in jobs. They may include:
- Job development and placement, matching individuals with positions suited to their abilities and interests.
- On-site job coaching, where a support professional helps with training, adapting to tasks, and building relationships with coworkers.
- Vocational training programs, preparing individuals with specific job skills in areas like hospitality, retail, or office work.
- Follow-along support, ensuring continued success in the workplace over time.
Meaningful employment fosters independence, boosts self-esteem, and provides financial and social benefits.
5. Residential Services
Housing options vary widely to accommodate different levels of independence and care needs. Options include:
- Group homes, staffed 24/7, offering a structured environment and full-time support.
- Supervised apartments, where individuals live more independently but still receive daily or weekly support.
- Shared living or host homes, where a person with disabilities lives with a host family or caregiver in a more personalized setting.
- Independent living training, teaching skills needed to manage personal finances, meal planning, housekeeping, and more.
Residential services prioritize safety, autonomy, and a sense of belonging.
6. Family Support and Respite Care
Families and caregivers are essential partners in care, and services are available to support their well-being too:
- Respite care, providing short-term relief to caregivers by temporarily placing the individual with another trusted provider — for a few hours, a weekend, or longer.
- Counseling and family therapy, helping relatives navigate emotional challenges, stress, and long-term planning.
- Parent training programs, equipping caregivers with skills and strategies to manage behavioral or developmental concerns at home.
- Peer support groups, where families can connect, share experiences, and build a community of understanding.
Strong support systems empower families and enhance the overall care network.
How Can Families Access These Services?
The first step is typically to contact a regional coordination center (such as Gateway Counseling Center in New York), where professionals guide families through the eligibility and assessment process. Once a diagnosis is confirmed, a personalized support plan can be developed that outlines the most appropriate services for intellectual disabilities.
Why Are These Services So Important?
Access to well-structured and personalized support allows individuals with intellectual disabilities to live more independent, fulfilling, and dignified lives. It also relieves pressure on families and moves society closer to true inclusivity and equality.